
All things business boil down to numbers so it’s vital they’re localized correctly for each market. Getting this wrong could mean an incorrect price point or a grossly inflated sales figure.
How complicated can it be and what could go wrong? Let’s find out.
What is number localization?
Number localization is the presentation of numbers in a format that adheres to the rules of a language. These rules can vary significantly so a small blunder could lead to a costly mistake.
In this article we’ll focus solely on number, but for more information about localizing units of measure read this article.
Worldwide number conventions
Here are some of the key differences to consider when localizing numbers:
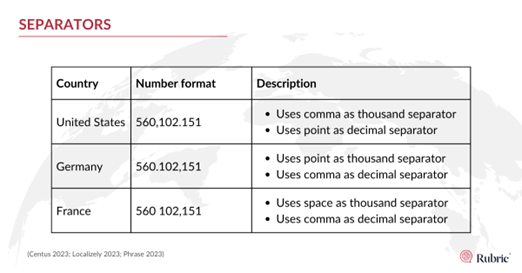
Separators:
Different languages use different separators to denote a decimal and thousand. Different languages use a space, a comma or a decimal point, but they don’t always have the same meaning!
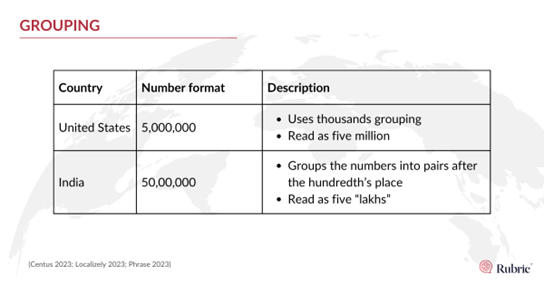
Grouping:
Numbers are also be grouped differently in different numerical systems. While most countries separate numbers into groups of thousands, India uses the “lakhs” and “crores” grouping system.
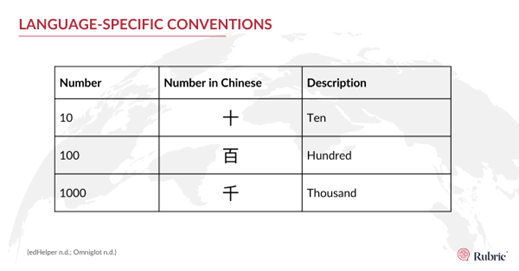
Digits:
Many languages use the 0 to 9 of the globally recognized Hindu-Arabic number system. But there are some exceptions. In Chinese, multiples of 10 (so thousands, millions, etc.) are represented by special characters.
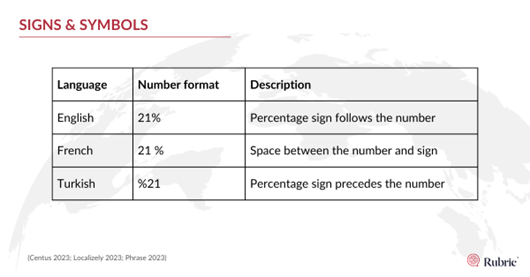
Signs and symbols:
The placement of signs, such as the percentage sign or arithmetic operators, may differ depending on the language. In Turkish, for example, the percentage sign precedes the number:
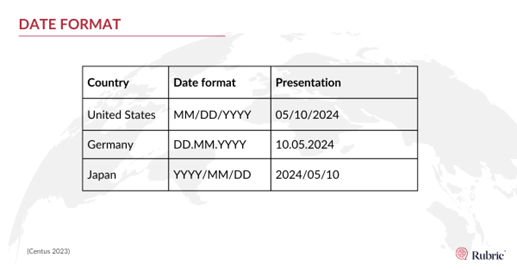
Date and time formats:
Date and time are represented in different formats worldwide. The 10th of May could be misread as the 5th of October if formats are ignored.
For time formats, some countries use the 12-hour format while others the 24-hour one. European countries typically follow the 24-hour format. Japan and India, on the other hand, follow the 12-hour clock accompanied by the notation for AM/PM.
How do you approach number localization?
Now you know how numbers and their formats can vary around the world, here are a few things to bear in mind when handling numbers and localization in general:
- Be aware of the different number conventions used.
- Ensure your website or software supports left-to-right and right-to-left language systems as this will affect how numbers are presented.
- Not all fonts are created equal. Use fonts that support the target language and number conventions you seek.
- Familiarize yourself with internationalization and localization standards, particularly if considering localizing global software.
- Ensure any units of measure are correctly localized.
- Be aware that in some industries the recognized standard worldwide is the use of US-English numeric rules, so make sure you’re aware of what’s expected in your specific industry.
More importantly, you don’t have to do this alone.
In business, the stakes can be high so, if in doubt, contact an expert.