
Did you know that there are over 120 languages and 19,500 dialects spoken in India?
India is a complex and diverse country. It also represents a huge potential for your global business… but only if you can localize your content effectively for the Indian market.
Knowing which languages you need to target is key if you want your company to have success in India's growing economy. With so many languages, the task of translation can seem overwhelming.
How can you know which languages to target?
How can you compare the many Indian languages?
How can you ensure you don't waste your localization budget?
If you're looking to expand your operations into India, it helps when you understand why language is such a complex topic.
Here's a helpful introduction to the languages in India and which represents the best business opportunity for you…
Should you target India as a market?
India is a vast and rapidly growing market for global companies.
It is expected that India will soon overtake China to become the most populous country in the world. It also has a booming economy and an increasing thirst for eCommerce.
However, doing business in India can be challenging.
One of the biggest challenges is the fact that there are so many languages in a single country. Individually, most of these languages only represent a small proportion of the business opportunity for the country… but together these many languages represent a huge potential.
If you can master the language challenges, you can benefit from the substantial opportunity that India represents.
Why language is complex in India
Global companies looking to expand into the Indian market face a complex task when it comes to languages and translation.
India has over 19,500 dialects with 121 languages, making it the most multilingual country in the world (although only 22 of these languages are officially recognized by the government).

English is widely spoken in India. However, it is not usually enough to keep your content in English.
According to research by Google and KPMG, 66% of internet users in India use local languages other than English. CSA Research also found that 44% of Indians online have trouble understanding product information and reviews in English.
All this means you must have a comprehensive localization strategy that considers the variety of languages spoken in the country. Localizing your products, services, and content into the most relevant languages for your target audiences can help you build trust and loyalty among Indian consumers.
When you understand the diversity of India's language landscape, you can develop a better localization strategy for success in India's growing economy.
Don't be fooled by the 2 official Indian languages
In many international markets, the "official languages" are a good place to start when you want to localize for the market. In some markets, you can safely reach most of the population by just localizing into the official languages.
This is not quite true in India.
India only has 2 official languages, which means those languages used for official government purposes:
- Hindi
- English
Some global companies look at this fact and think that they only need to support Hindi and English to give them enough coverage in India. This could not be further from the truth.
The 22 national languages in India
India also has 22 officially recognized "national" languages that are spoken as the dominant language in various states.
These 22 national languages, arranged in alphabetical order, are:
1. Assamese -- spoken in the regions of Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
2. Bengali -- spoken in West Bengal and Tripura.
3. Bodo -- spoken in Assam.
4. Dogri -- official language of Jammu and Kashmir.
5. Gujarati -- spoken in Dadra, Nagar Haveli, Daman, and Diu, Gujarat.
6. Hindi -- spoken in many regions including Deli, Gujarat, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
7. Kannada — spoken in Karnataka.
8. Kashmiri -- spoken in Jammu and Kashmir.
9. Konkani -- spoken in various regions including Goa, Karnataka, and Kerala.
10. Maithili -- spoken in Bihar and Jharkhand.
11. Malayalam -- spoken in Kerala, Lakshadweep, and Puducherry.
12. Manipuri -- spoken in Manipur.
13. Marathi -- spoken in various regions including Maharashtra, Dadra, and Nagar Haveli.
14. Nepali -- spoken in Sikkim and West Bengal.
15. Odia -- official language of Orissa.
16. Punjabi -- official language of Punjab and Chandigarh.
17. Sanskrit — spoken in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
18. Santali — spoken by Santhal people mainly in the state of Jharkhand as well as in other regions.
19. Sindhi -- spoken mainly in Gujarat and Maharashtra.
20. Tamil -- spoken in Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
21. Telugu -- spoken in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Puducherry
22. Urdu -- spoken in various regions, including Telangana, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
However, this is just the beginning of languages spoken in India. Besides these 22 official national languages, there are around 100 more languages used to various degrees, and thousands more dialects.
Which languages you choose for your company's content will depend hugely on which regions you want your company to succeed in. For example, if you want to target the state of Kerala, 96.6% of people speak Malayalam.
Languages in India: The maps
When you look at the map of India, you can see how the languages are spoken in each state, as well as the variations within those languages.
This can be especially beneficial when looking to target specific regions of India for expansion.
Here are the language families spoken in India (CC-BY-SA)…
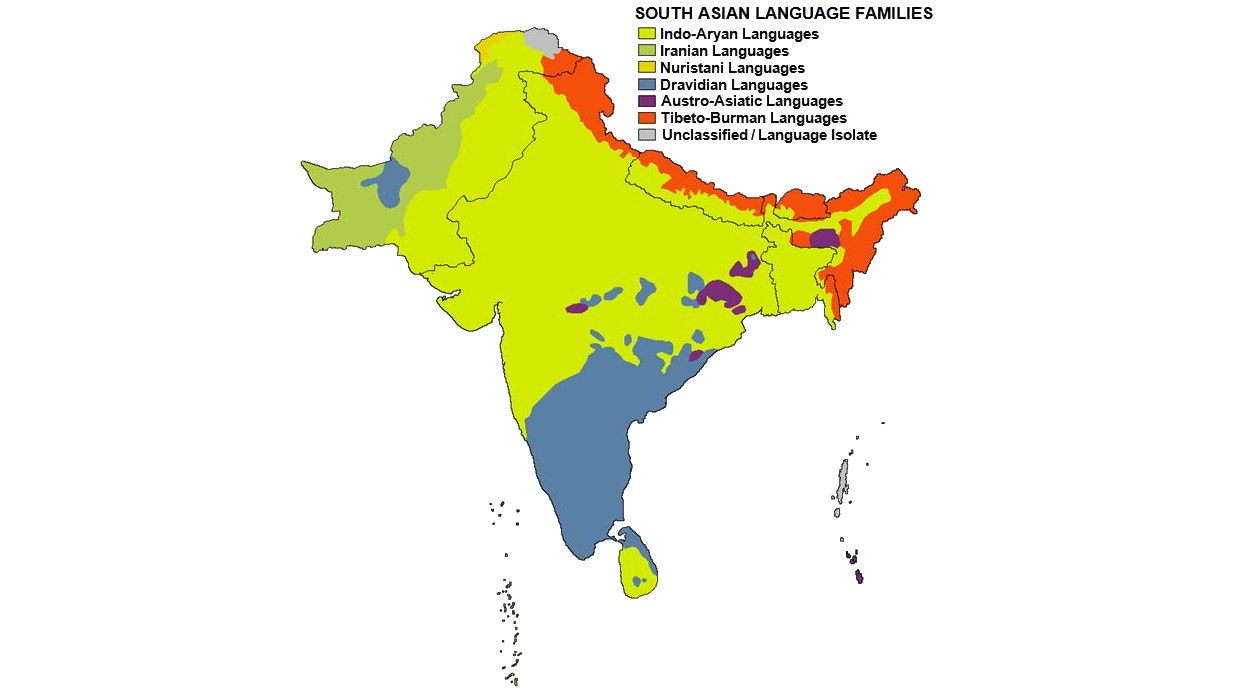
and the primary languages spoken in particular states and regions (CC-BY-SA)…
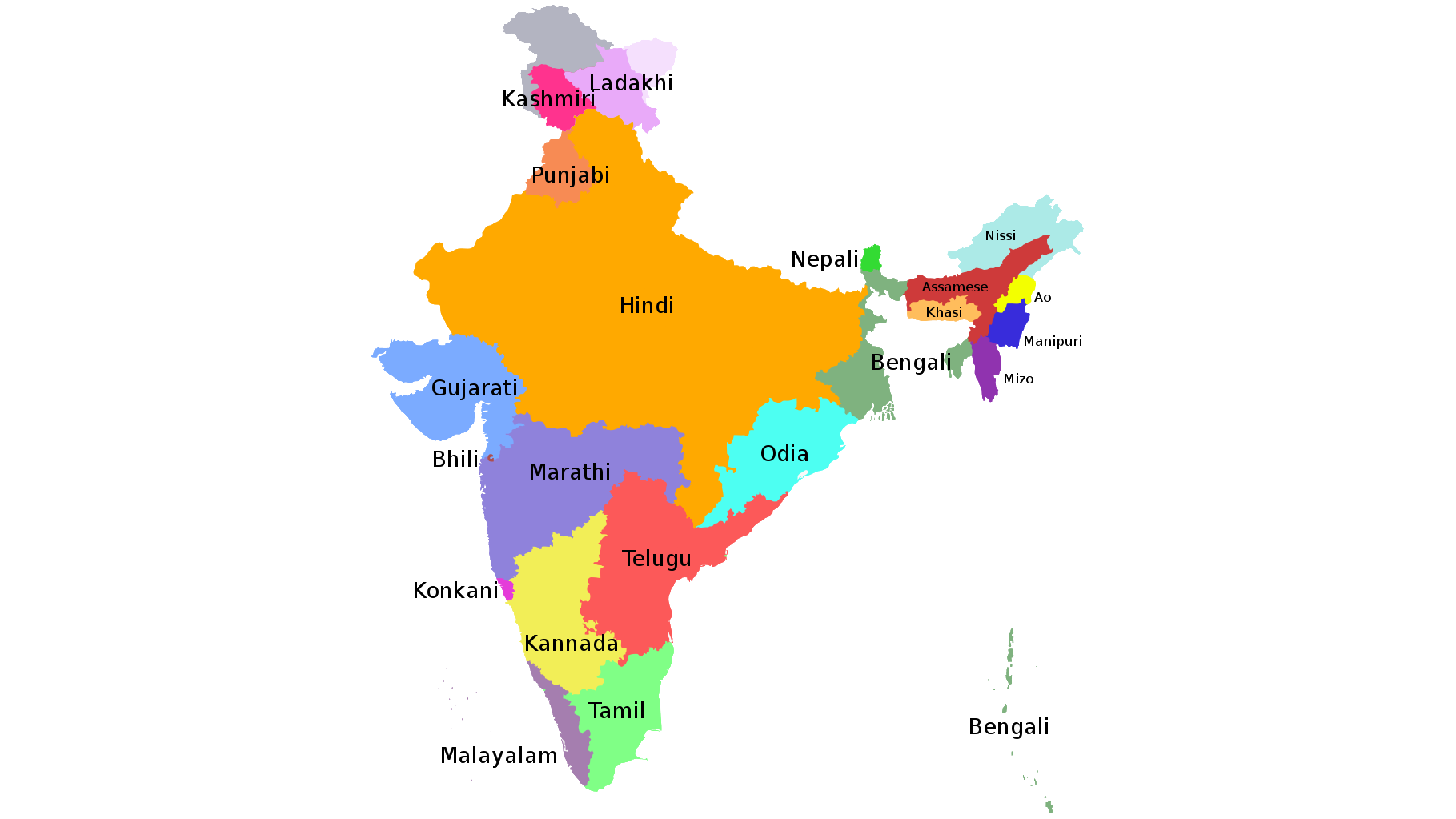
The path to success when localizing your content for India is to think in terms of the states and regions that you want to target.
How to decide between all the Indian languages
With 19,500 languages in the country, how can you possibly translate your content for the Indian market?
Even just considering the 22 officially recognized national languages can be overwhelming. Translating into all 22 languages could quickly become cost-prohibitive.
You need a way to compare the languages for your translation…
Why "number of speakers" is not an ideal comparison
One way to compare languages is by looking at the number of speakers of each across the country. By this measure, you might assume you could reach 80% of the population by supporting 7 languages: Hindi, English, Bengali, Marathi, Telugu, Tamil, and Urdu.
In reality, supporting speakers of a language might not be the best measure for online success. Just because people are speaking a language doesn't mean they are navigating the internet or buying products in this language.
Digital opportunity: A better comparison
For many companies, a better way to compare languages is to look at the business opportunity each language represents.
One way to compare languages is to look at each language's "digital opportunity" rating by CSA Research.
This is a measure of the language's reach and potential for digital marketing, looking at the language by 3 factors:
- eGDP — What percentage of the "electronic gross domestic product" (eGDP) the language commands. A higher value means more potential for income.
- Online Population — What percentage of the total global online population the language commands. A higher value means more people reached.
- Brand Support — The percentage of support that the language has on brand websites. A lower value could suggest a lucrative untapped market with little competition.
CSA Research lists 8 Indian languages in its Tier 1-3 languages (those with the most digital opportunity):
- Hindi -- eGDP: 1.4%; Online population: 0.7%; Brand support: 23.2%
- Bengali -- eGDP: 0.36%; Online population: 2.1%; Brand support: 0.9%
- Urdu -- eGDP: 0.25%; Online population: 1%; Brand support: 0.8%
- Telugu -- eGDP: 0.21%; Online population: 1.28%; Brand support: 0.5%
- Marathi -- eGDP: 0.2%; Online population: 1.24%; Brand support: 0.6%
- Tamil -- eGDP: 0.21%; Online population: 1%; Brand support: 0.8%
- Gujarati -- eGDP: 0.13%; Online population: 0.77%; Brand support: 0.6%
- Kannada -- eGDP: 0.13%; Online population: 0.77%; Brand support: 0.6%
Some of these numbers may look low at first glance. However, remember that these are percentages of the entire online global population. Even a fraction of a percentage can represent a significant business opportunity.

For example, a significant amount of people speaks the language of Marathi in South-Western regions. It is the third most spoken and understood language throughout the country.
Marathi also has very low global brand support with 0.6%, which suggests low competition. Even though it only represents 0.2% of the global online GDP, if your company was to target the state of Maharashtra, for example, this could give you a significant advantage in India's second most populous state.
Such decisions are not simple to make. There are lots of factors. This is why it's so important to think strategically when you decide to move into India as a market.
How to navigate India's 19,500 languages
The sheer number of languages spoken in India may seem daunting. But, when you understand the language landscape, you can make better decisions about your company's localization efforts.
Knowing which languages you will target is the first step to developing a strong localization process for the Indian market.
You almost certainly won't be able to translate into all 19,500 of India's languages and dialects. However, when you approach localization strategically, you can make benefit from this growing and lucrative economy.
Start by identifying the regions you want to target.